Emulsifiers in food and feed explained
From bread to beauty cream and from mayonnaise to margarine. Emulsifiers are indispensable in our daily lives. As a 'binding agent' of oil and water, they keep emulsions stable. One of the oldest emulsifiers is lecithin (extracted from egg yolk), but castor oil ethoxylates are at least as valuable.
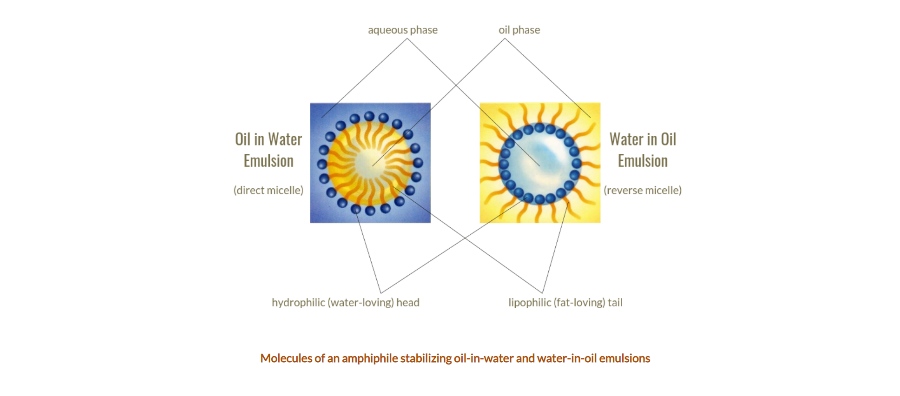
An emulsion is a mixture of oil and water. Emulsions can be divided into two categories: Water-in-oil emulsions which contain small water droplets that are dispersed in oil. And oil-in-water emulsions which contain small oil droplets that are dispersed in water. In both cases, the emulsifier ensures that the mixture is stable and prevents the oil and water from separating into two layers. But an emulsifier has also the functionality:
- a better structure and texture
- preservation of quality and freshness
- prevention of the growth of moulds
Emulsifiers are widely used in both the food and feed industries.
Lecithin (E322)
Lecithin is one of the oldest emulsifiers. It is found in egg yolk (the Greek word for egg yolk is lecithos) and is used, for example, to make mayonnaise. This so-called phospholipid is a unique compound that contains soluble fat and water. Lecithin can be extracted from vegetable oils and converted into a liquid or (dry) powder.
In addition to the functional benefits it adds to our daily food, lecithin also has remarkable health benefits. It helps with the proper functioning of our cholesterol, liver, cardiovascular system, brain and gallbladder, to name a few.
Castor oil ethoxylates (E484)
Castor oil ethoxylates form part of an essential class of emulsifiers. They are found in many applications and in different market segments. The oil, which is extracted from the seed of the Castor plant (Ricinus communis), is processed via ethoxylation. This process gives distinctive physical properties that can impart surface-active properties to a product.
These properties ultimately enable ethoxylated castor oils to bind two immiscible materials (e.g. oil and water). In short, a proper and wide applicable emulsifier.
HLB Index: Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance
HLB indicates the predicted preference of an emulsifier for oil or water. The higher the HLB value, the more the molecule is drawn to water (hydrophilic). The lower the HLB value, the more water-repellent the molecule is (hydrophobic).
- <10: Soluble in lipids (insoluble in water)
- >10: Soluble in water (insoluble in lipids)
- 3 to 6: W / O (water-in-oil) emulsifier
- 7 to 9: wetting and spreading agent
- 8 to 16: O / W (oil-in-water) emulsifier
The most commonly used emulsifiers in today's food and feed are:
- Lecithin (Soya & Sunflower) (E322)
- Castor oil ethoxylates (synonym: Castor oil -n-polyglycol ether) (E484)
- CITREM (E471c)
- DATEM (E471e)
- Glyceryl Mono Oleate (E471)
- Sorbitan Mono Laurate (E493)
- Polysorbates (E432-E436)
- Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate (E476)
Do you have an interest in these products, please contact the responsible sales manager.